Endobronchial coils
Educational Material:
- Lung volume reduction coil treatment for patients with severe emphysema: a European multicentre trial. Deslee G et al. Thorax 2014;69(11):980-6
- Bronchoscopic Nitinol Coil Implantation – A New Lung Volume Reduction Strategy in COPD. Kontogianni K et al. EMJ 2013;1:72-78
- Late Major Hemoptysis After Lung Volume Reduction With Coils Induced by Dual Antiaggregation Therapy. Valenti A et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2016;101(2):e49-50
Coils are implantable devices composed of preformed nitinol wire (shape memory). The wire is straightened before delivery. It is delivered through a flexible bronchoscope in a subsegmental bronchus. It takes its initial shape after deployment.
- The bronchoscope is positioned in the selected airway
- A guidewire is advanced under fluoroscopy guidance
- The catheter is advanced over the guidewire (distal tip approximately 15mm from the pleura)
- The length of the airway is measured with the help of radiopaque markers and the appropriate coil size is chosen
- The guidewire is removed and the catheter remains in place
- The coil is taken with the forceps and is passed through the cartridge (straightening of the coil)
- The coil is loaded into the distal end of the catheter (coupling the cartridge to the catheter´s hub), it is then advanced through the catheter
- The catheter is removed and the coil is released
- The coil takes its initial shape
- The airway is mechanically bent and the lung parenchyma is compressed
- Several coils are deployed. The objective is to obtain an equal subsegmental distribution throughout the treated lobe.
The main complications are pneumothorax, pulmonary hemorrage, infectious exacerbation
- Lung volume reduction coil treatment for patients with severe emphysema: a European multicentre trial. Deslee G et al. Thorax 2014;69(11):980-6
- Bronchoscopic Nitinol Coil Implantation – A New Lung Volume Reduction Strategy in COPD. Kontogianni K et al. EMJ 2013;1:72-78
- Late Major Hemoptysis After Lung Volume Reduction With Coils Induced by Dual Antiaggregation Therapy. Valenti A et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2016;101(2):e49-50
Coils are implantable devices composed of preformed nitinol wire (shape memory). The wire is straightened before delivery. It is delivered through a flexible bronchoscope in a subsegmental bronchus. It takes its initial shape after deployment.
- The bronchoscope is positioned in the selected airway
- A guidewire is advanced under fluoroscopy guidance
- The catheter is advanced over the guidewire (distal tip approximately 15mm from the pleura)
- The length of the airway is measured with the help of radiopaque markers and the appropriate coil size is chosen
- The guidewire is removed and the catheter remains in place
- The coil is taken with the forceps and is passed through the cartridge (straightening of the coil)
- The coil is loaded into the distal end of the catheter (coupling the cartridge to the catheter´s hub), it is then advanced through the catheter
- The catheter is removed and the coil is released
- The coil takes its initial shape
- The airway is mechanically bent and the lung parenchyma is compressed
- Several coils are deployed. The objective is to obtain an equal subsegmental distribution throughout the treated lobe.
The main complications are pneumothorax, pulmonary hemorrage, infectious exacerbation
-
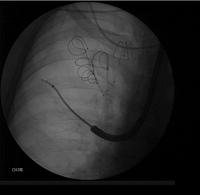
Lung volume reduction with coils: the guidewire is advanced to the targeted area
-
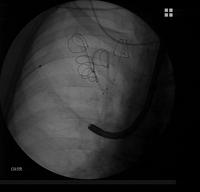
Lung volume reduction with coils: the guidewire has been removed and the catheter remains in place
-
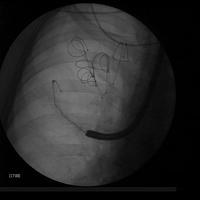
Lung volume reduction with coils: the coil is being deployed
-
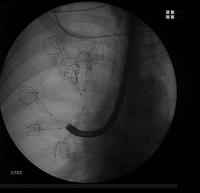
Lung volume reduction with coils: the coil has been completely deployed
